Leave out the fixed costs (labor, electricity, machinery, utensils, etc). Break even point (BEP) refers to the activity level at which total revenue equals total cost. Contribution margin is the variable expenses plus some part of fixed costs which is covered. Thus, CM is the variable expense plus profit which will incur if any activity takes place over and above BEP. Crucial to understanding contribution margin are fixed costs and variable costs.
Fixed cost vs. variable cost
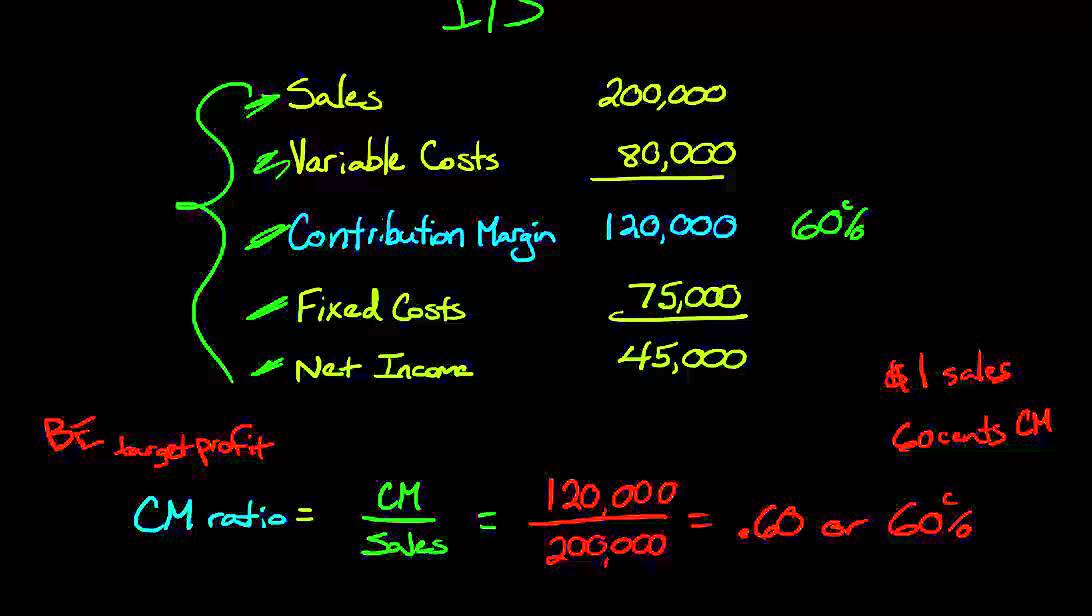
In the same example, CMR per unit is $100-$40/$100, which is equal to 0.60 or 60%. So, 60% of your revenue is available to cover your fixed costs and contribute to profit. Now, this situation can change when your level of production increases. As mentioned above, the per unit variable cost decreases with the increase in the level of production. Direct Costs are the costs that can be directly identified or allocated to your products. For instance, direct material cost and direct labor cost are the costs that can be directly allocated with producing your goods.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
For a quick example to illustrate the concept, suppose there is an e-commerce retailer selling t-shirts online for $25.00 with variable costs of $10.00 per unit. While there are plenty of profitability metrics—ranging from the gross margin down to the net profit margin—the contribution margin metric stands out for the analysis of a specific product or service. The contribution margin may also be expressed as fixed costs plus the amount of profit. To cover the company’s fixed cost, this portion of the revenue is available.
Business Cards
We would consider the relevant range to be between one and eight passengers, and the fixed cost in this range would be \(\$200\). If they exceed the initial relevant range, the fixed costs would increase to \(\$400\) for nine to sixteen passengers. In effect, the process can be more difficult in comparison edsel dope to a quick calculation of gross profit and the gross margin using the income statement, yet is worthwhile in terms of deriving product-level insights. Using the provided data above, we can calculate the price per unit by dividing the total product revenue by the number of products sold.
20: Contribution Margin Ratio
- In our example, the sales revenue from one shirt is \(\$15\) and the variable cost of one shirt is \(\$10\), so the individual contribution margin is \(\$5\).
- Instead, management uses this calculation to help improve internal procedures in the production process.
- The contribution margin is affected by the variable costs of producing a product and the product’s selling price.
- For those organizations that are still labor-intensive, the labor costs tend to be variable costs, since at higher levels of activity there will be a demand for more labor usage.
- In the Dobson Books Company example, the contribution margin for selling $200,000 worth of books was $120,000.
It is important for you to understand the concept of contribution margin. This is because the contribution margin ratio indicates the extent to which your business can cover its fixed costs. That said, most businesses operate with contribution margin ratios well below 100%. However, the growing trend in many segments of the economy is to convert labor-intensive enterprises (primarily variable costs) to operations heavily dependent on equipment or technology (primarily fixed costs).

Fixed costs are production costs that remain the same as production efforts increase. Variable costs, on the other hand, increase with production levels. The Contribution Margin is the incremental profit earned on each unit of product sold, calculated by subtracting direct variable costs from revenue. The contribution margin represents the revenue that a company gains by selling each additional unit of a product or good.
Based on the contribution margin formula, there are two ways for a company to increase its contribution margins; They can find ways to increase revenues, or they can reduce their variable costs. Fixed costs are costs that are incurred independent of how much is sold or produced. Buying items such as machinery is a typical example of a fixed cost, specifically a one-time fixed cost. Regardless of how much it is used and how many units are sold, its cost remains the same.
If you were to manufacture 100 new cups, your total variable cost would be $200. However, you have to remember that you need the $20,000 machine to make all those cups as well. In accounting, contribution margin is the difference between the revenue and the variable costs of a product. It represents how much money can be generated by each unit of a product after deducting the variable costs and, as a consequence, allows for an estimation of the profitability of a product. The first step to calculate the contribution margin is to determine the net sales of your business.
